If untreated a cholesteatoma can eat into the three small bones located in the middle ear the malleus incus and stapes collectively called ossicles which can result in nerve deterioration deafness imbalance and vertigo.
Attic cholesteatoma radiopaedia.
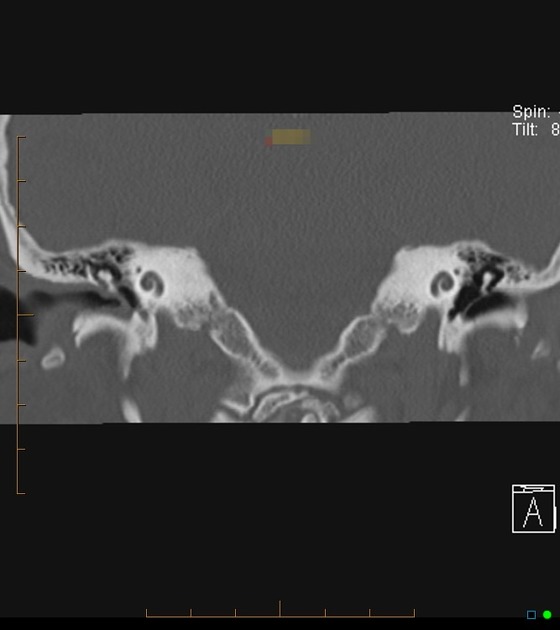
Soft tissue occupying the right middle ear involving prussak spaces and the attic.
Conventional non contrast mr imaging with diffusion weighted imaging is recommended in all patients with a suspicion of cholesteatoma.
Normally aerated mastoid air cells.
The mass extends superiorly into the attic and appears to have eroded through the tegmentum as well as through the fallopian canal of the facial nerve and perhaps the lateral semicircular canal.
Hrct of the temporal bone has an excellent spatial resolution thus even small soft tissue lesions can be accurately.
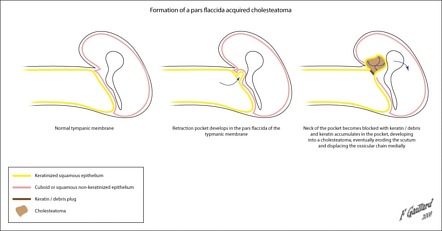
A cholesteatoma is an abnormal sac of keratinizing squamous epithelium and accumulation of keratin within the middle ear or mastoid air cell spaces which can become infected and also erode neighbouring structures.
An mri should be performed especially in patients with previous surgery for cholesteatoma since recurrence or residual tumor can be detected with great accuracy.
Findings are characteristic of an acquired cholesteatoma.
If the cholesteatoma has been dry the cholesteatoma may present the appearance of wax over the attic.
The external acoustic canal is a rare location for a cholesteatoma with an estimated incidence around 1 2 per 1 000 new otological patients.
Radiopaedia is free thanks to our supporters and advertisers.
Upon reaching the posterolateral wall of the attic further expansion of the cholesteatoma is deflected superiorly toward the aditus ad antrum and mastoid antrum.
However the sequence is prone to artefact and care must be taken how the sequence is performed and interpreted 2.
As the cholesteatoma fills the aditus ad antrum the adjacent lateral semicircular canal is at risk.
The tegmentum tympani is intact.
Diffusion weighted imaging is particularly useful when distinguishing a cholesteatoma from other middle ear masses.
It is the only entity that demonstrates high signal intensity on dwi.
The relevant aspects of cholesteatomas are reviewed with the emphasis on their diagnosis by using cross sectional imaging.
The indications and limitations of ct and mr imaging and the use of novel mr imaging techniques in the diagnosis of cholesteatomas are described.
The attic is just above the eardrum.
This case is a histologically proven case of cholesteatoma.
The overall incidence rate in one large study was 0 30 per year per 100 000 inhabitants 1.
For comparison the annual incidence of middle ear cholesteatoma is around 9 2 per 100 000.
Erosion of the malleus and incus as well as the scutum.